LEWI: Wi-Fi Mapping for Enclosed Spaces
Mapping
Signal Processing
Microcontrollers
MATLAB
LEWI (Localization of Enclosed spaces using Wi-Fi) explores compressive sensing techniques that leverage the propagation of Wi-Fi signals through obstacles to reconstruct occluded environments for cooperative robot teams.
Objective
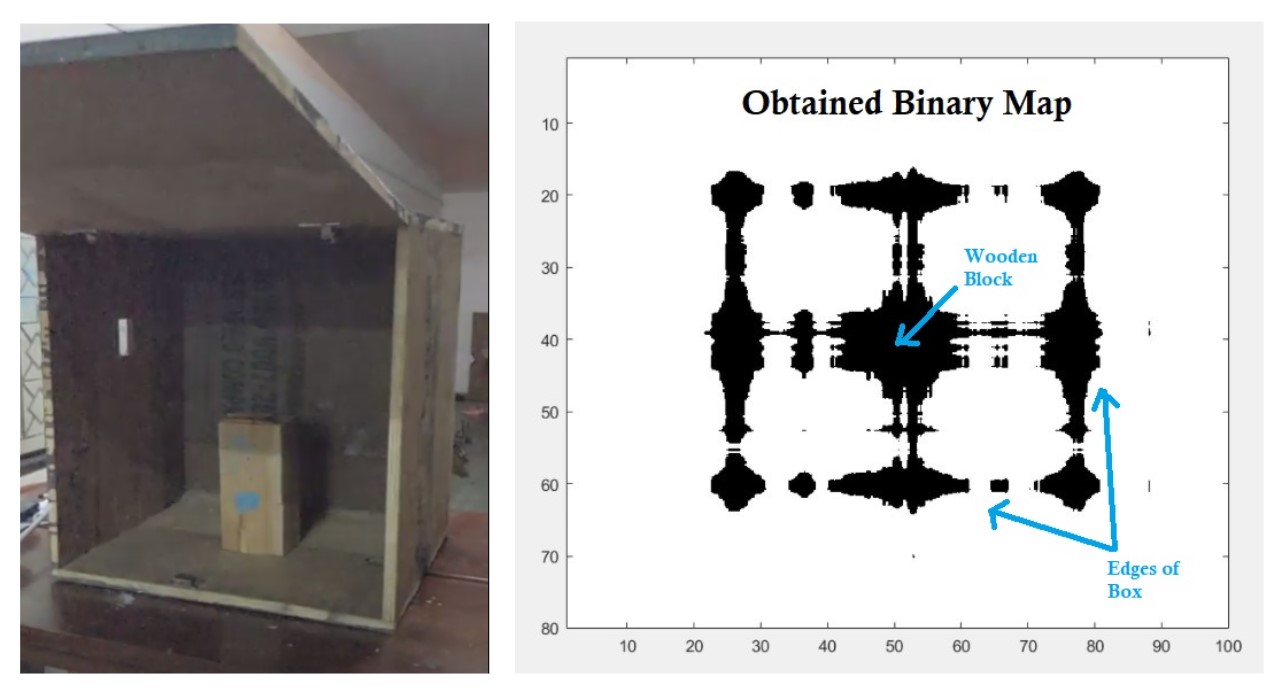
Guided the development of an obstacle mapping pipeline capable of reconstructing hidden geometry in enclosed spaces, enabling UAV swarms to maintain situational awareness despite occlusions and limited sensor coverage.
Technology Stack
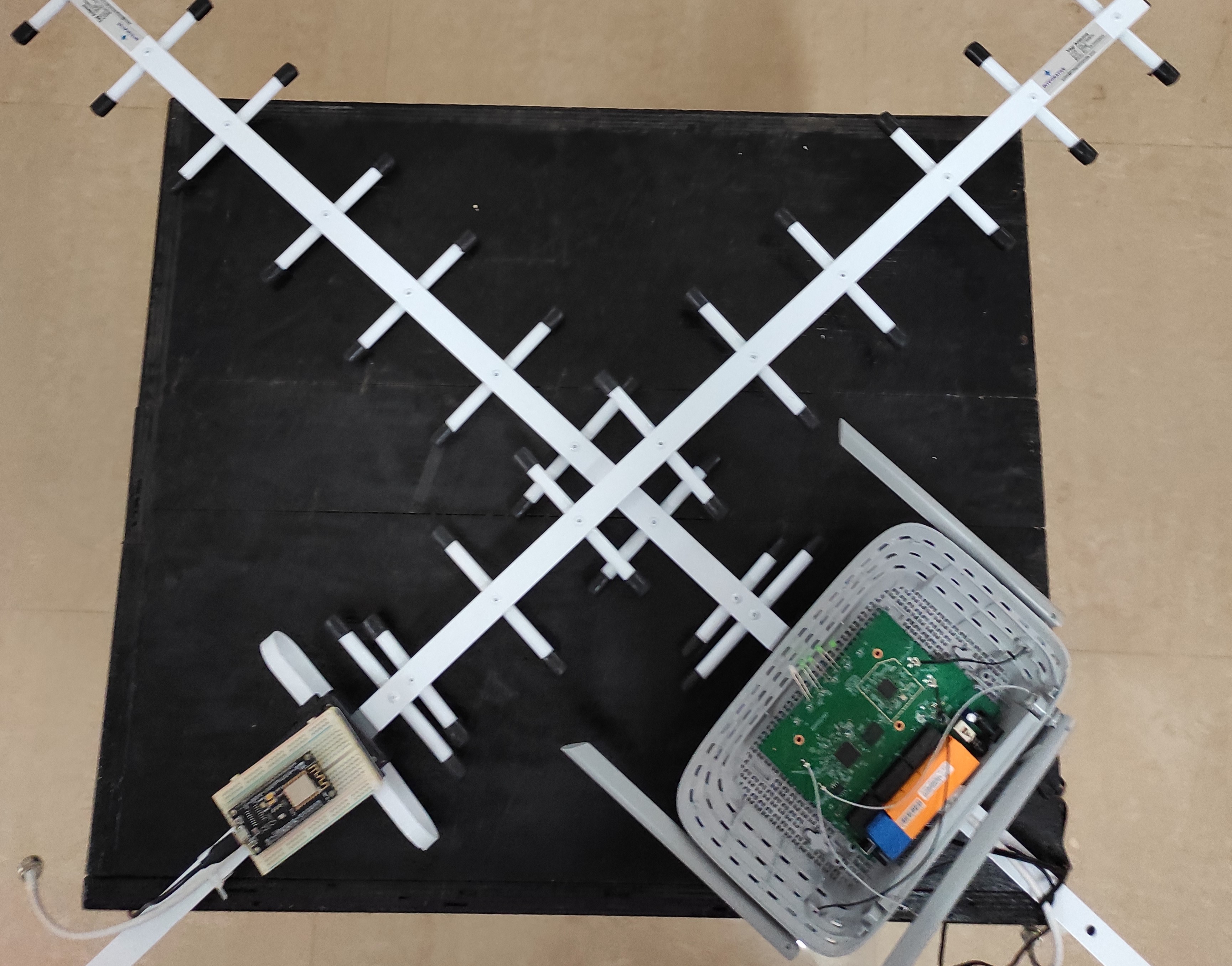
- ESP8266 nodes for Wi-Fi beaconing and signal capture.
- Compressive sensing algorithms to infer structure from sparse measurements.
- Directional Yagi antennas to study signal attenuation across materials.
- MATLAB-based reconstruction tools tuned for cooperative robot deployment.
Key Features
- Reconstructs occluded obstacles by analyzing Wi-Fi signal decay and multi-path behavior.
- Designed for collaborative UAV mapping missions under strict time budgets.
- Minimizes required measurements while preserving localization fidelity for delay-sensitive tasks.
- Determines both location and approximate shape of obstacles that traditional sensors miss.
Impact
Demonstrated that low-cost networking hardware combined with signal processing can augment conventional SLAM stacks, equipping autonomous teams with robust perception in cluttered indoor environments.