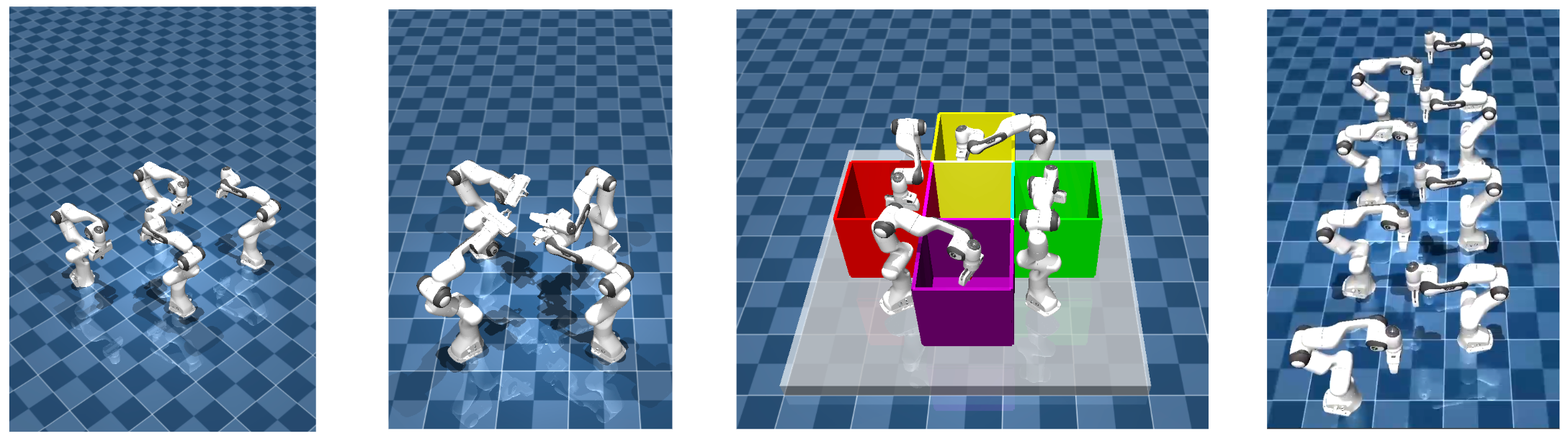
Accelerating Search-Based Planning for Multi-Robot Manipulation by Leveraging Online-Generated Experiences
C++
Lattice-Based Search
Conflict-Based Search
Multi-Agent Path Planning
High Dimensional Planning
MuJoCo
Research Objective
Coordinating multiple robotic manipulators in shared workspaces is a significant computational challenge, typically requiring planners to solve each query from scratch. This project involved the from-scratch implementation and benchmarking of a suite of planning algorithms—including RRT-Connect, Conflict-Based Search (CBS), and Enhanced Conflict-Based Search (ECBS)—against a novel experience-accelerated variant, xECBS. By leveraging an online-generated experience database to provide "warm starts" for low-level searches, the algorithm aims to significantly reduce planning time in structured environments while maintaining bounded suboptimality and completeness guarantees for high-dimensional multi-robot systems.
Key Features Achieved
- Suite Implementation from Scratch: Developed full C++ implementations of CBS (A* low-level), ECBS (Weighted A* focal search), and xECBS within the MuJoCo physics engine, utilizing a lattice-based graph construction for the 7-DOF joint spaces.
- Experience-Accelerated Search: Integrated online experience reuse into the CBS paradigm, accelerating individual robot searches by injecting relevant past path segments directly into the search tree's OPEN list.
- Multi-Arm Coordination: Successfully scaled to coordinate up to eight 7-DOF Franka Emika Panda arms, effectively navigating a 56-dimensional composite configuration space with high geometric coupling.
- Physics-Aware Planning: Developed a high-fidelity collision checking pipeline in MuJoCo, approximating robot links with spheres and capsules for optimized analytical distance computations during search.
Challenges & Benchmarking
- RRT-Connect Failure in High-D: Benchmarking revealed that RRT-Connect fails to find solutions in the majority of high-dimensional multi-arm queries, highlighting the necessity of structured search-based methods for coordinated manipulation.
- Scalability Degradation: Traditional search-based methods like ECBS showed significant performance decay as the system scaled from 4 to 8 robots, with planning times increasing by nearly an order of magnitude.
- Geometric Complexity: Managed tightly coupled "criss-cross" configurations where narrow passages in the joint space cause standard CBS to frequently time out or fail.
- Theoretical Guarantees: Proved that xECBS maintains the completeness and bounded suboptimality (w = 1.5) of ECBS while providing substantial computational speedups.
Quantitative Results
- Massive Speedups: In the 8-arm scene, xECBS achieved a mean planning time of 136.81s, outperforming standard ECBS (462.79s) by over 3.3x.
- Superior Reliability: Successfully solved 100% of "criss-cross" and 8-arm scenarios within the time limit, whereas RRT-Connect achieved only a 10% success rate in even simpler random configurations.
- Efficiency Gains: Achieved lowest mean planning time (18.43s) in random configurations—roughly 1.1x faster than CBS and 2x faster than ECBS—while maintaining solution quality within 10-15% of optimal cost.